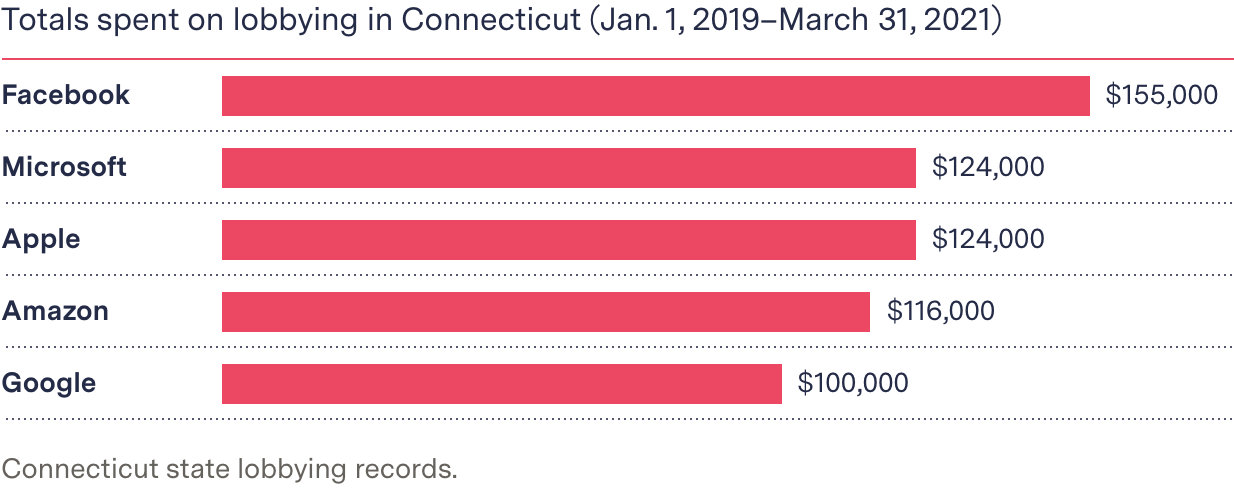Concerned about growing momentum behind efforts to regulate the commercial use of personal data, Big Tech has begun seeding watered-down “privacy” legislation in states with the goal of preempting greater protections, experts say.
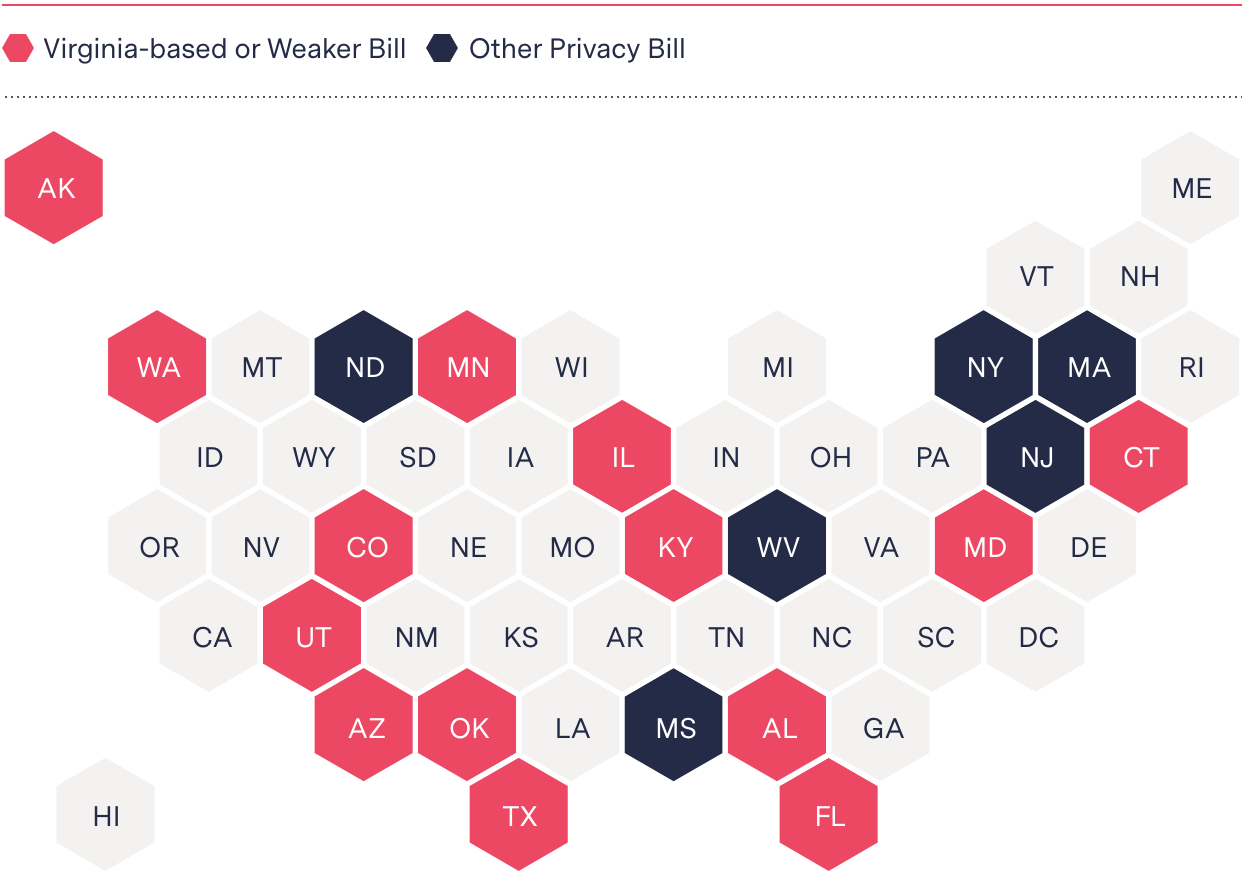
The swift passage in March of a consumer data privacy law in Virginia, which Protocol reported was originally authored by Amazon with input from Microsoft, is emblematic of an industry-driven, lobbying-fueled approach taking hold across the country. The Markup reviewed existing and proposed legislation, committee testimony, and lobbying records in more than 20 states and identified 14 states with privacy bills built upon the same industry-backed framework as Virginia’s, or with weaker models. The bills are backed by a who’s who of Big Tech–funded interest groups and are being shepherded through statehouses by waves of company lobbyists.
Fourteen of 20 proposed state privacy bills were built upon the same industry-backed framework as Virginia’s, or weaker
States with proposals for privacy bills, by type
Meanwhile, the small handful of bills that have not adhered to two key industry demands—that companies can’t be sued for violations and consumers would have to opt out of rather than into tracking—have quickly died in committee or been rewritten.
See the state privacy bills here.
Experts say Big Tech’s push to pass friendly state privacy bills ramped up after California enacted sweeping privacy bills in 2018 and 2020—and that the ultimate goal is to prompt federal legislation that would potentially override California’s privacy protections.
“The effort to push through weaker bills is to demonstrate to businesses and to Congress that there are weaker options,” said Ashkan Soltani, a former chief technologist for the Federal Trade Commission who helped author the California legislation. “Nobody saw Virginia coming. That was very much an industry-led effort by Microsoft and Amazon. At some point, if multiple states go the way of Virginia, you might not even get companies to honor California’s [rules].”
California’s laws, portions of which don’t go into effect until 2023, create what is known as a “global opt out.” Rather than every website requiring users to go through separate opt-out processes, residents can use internet browsers and extensions that automatically notify every website that a user wishes to opt out of the sale of their personal data or use of it for targeted advertising—and companies must comply. The laws also allow consumers to sue companies for violations of the laws’ security requirements and created the California Privacy Protection Agency to enforce the state’s rules.
“Setting up these weak foundations is really damaging and really puts us in a worse direction on privacy in the U.S.,” said Hayley Tsukayama, a legislative activist for the Electronic Frontier Foundation. “Every time that one of these bills passes, Virginia being a great example, people are saying ‘This is the model you should be looking at, not California.’ ”
Amazon did not respond to requests for comment, and Microsoft declined to answer specific questions on the record.
Industry groups, however, were not shy about their support for the Virginia law and copycats around the country.
The Virginia law is a “ business and consumer friendly approach” that other states considering privacy legislation should align with, The Internet Association, an industry group that represents Big Tech, wrote in a statement to The Markup.
Big Tech’s Fingerprints Are All Over State Privacy Fights
In testimony before lawmakers, tech lobbyists have criticized the state-by-state approach of making privacy legislation and said they would prefer a federal law. Tech companies offered similar statements to The Markup.
Google spokesperson José Castañeda declined to answer questions but emailed The Markup a statement: “As we make privacy and security advancements to protect consumers, we’ll continue to advocate for sensible data regulations around the world, including strong, comprehensive federal privacy legislation in the U.S.”
But at the same time, the tech and ad industries have taken a hands-on approach to shape state legislation. Mostly, industry has advocated for two provisions. The first is an opt-out approach to the sale of personal data or using it for targeted advertising, which means that tracking is on by default unless the customer finds a way to opt out of it. Consumer advocates prefer privacy to be the default setting, with users given the freedom to opt in to certain uses of their data. The second industry desire is preventing a private right of action, which would allow consumers to sue for violations of the laws.
The industry claims such privacy protections are too extreme.
“That may be a bonanza for the trial bar, but it will not be good for business,” said Dan Jaffe, group executive vice president for government relations for the Association of National Advertisers, which has lobbied heavily in states and helped write model federal legislation. TechNet, another Big Tech industry group that has been deeply engaged in lobbying state lawmakers, said that “enormous litigation costs for good faith mistakes could be fatal to businesses of all sizes.”
Through lobbying records, recordings of public testimony, and interviews with lawmakers, The Markup found direct links between industry lobbying efforts and the proliferation of these tech-friendly provisions in Connecticut, Florida, Oklahoma, and Washington. And in Texas, industry pressure has shaped an even weaker bill.
Protocol has previously documented similar efforts in Arizona, Hawaii, Illinois, and Minnesota.
Additionally, The Markup found a handful of states—particularly North Dakota and Oklahoma—in which tech lobbyists have stepped in to thwart efforts to enact stricter laws.
Connecticut
The path of Connecticut’s bill is illustrative of how these battles have played out. There, state Senate majority leader Bob Duff introduced a privacy bill in 2020 that contained a private right of action. During the bill’s public hearing last February, Duff said he looked out on a room “literally filled with every single lobbyist I’ve ever known in Hartford, hired by companies to defeat the bill.”
The legislation failed. Duff introduced a new version of it in 2021, and it too died in committee following testimony from interest groups funded by Big Tech, including the Internet Association and The Software Alliance.
It’s an uphill battle because you’re fighting a lot of forces on many fronts. They’re well funded, they’re well heeled, and they just hire a lot of lobbyists….
Majority Leader Bob Duff, Conn. state Senate
According to Duff and Sen. James Maroney, who co-chairs the Joint Committee on General Law, those groups are now pushing a separate privacy bill, written using the Virginia law as a template. Duff said lawmakers “had a Zoom one day with a lot of big tech companies” to go over the bill’s language.
“Our legislative commissioner took the Virginia language and applied Connecticut terminology,” Maroney said.
That industry-backed bill passed through committee unanimously on March 23.
“It’s an uphill battle because you’re fighting a lot of forces on many fronts,” Duff said. “They’re well funded, they’re well heeled, and they just hire a lot of lobbyists to defeat legislation for the simple reason that there’s a lot of money in online data.”
Google has spent $100,000 lobbying in Connecticut since 2019, when Duff first introduced a consumer data privacy bill. Apple and Microsoft have each spent $124,000, Amazon has spent $116,000, and Facebook has spent $155,000, according to the state’s lobbyist reporting database.
Microsoft declined to answer questions and instead emailed The Markup links to the testimony its company officials gave in Virginia and Washington.
The Virginia model “is a thoughtful approach to modernize United States privacy law, something which has become a very urgent need,” Ryan Harkins, the company’s senior director of public policy, said during one hearing.
Google declined to respond to The Markup’s questions about their lobbying. Apple and Amazon did not respond to requests for comment.
Oklahoma
In Oklahoma, Rep. Collin Walke, a Democrat, and Rep. Josh West, the Republican majority leader, co-sponsored a bill that would have banned businesses from selling consumers’ personal data unless the consumers specifically opted in and gave consumers the right to sue for violations. Walke told The Markup that the bipartisan team found themselves up against an army of lobbyists from companies including Facebook, Amazon, and leading the effort, AT&T.
AT&T lobbyists persuaded House leadership to delay the bill’s scheduled March 2 hearing, Walke said. “For the whole next 24-hour period, lobbyists were pulling members off the house floor and whipping them.”
Walke said to try to get the bill through the Senate, he agreed to meetings with Amazon, internet service providers, and local tech companies, eventually adopting a “Virginia-esque” bill. But certain companies remained resistant—Walke declined to specify which ones—and the bill died without receiving a hearing.
AT&T did not respond to questions about its actions in Oklahoma or other states where it has fought privacy legislation. Walke said he plans to reintroduce the modified version of the bill again next session.
Texas
In Texas, Rep. Giovanni Capriglione first introduced a privacy bill in 2019. He told The Markup he was swiftly confronted by lobbyists from Amazon, Facebook, Google, and industry groups representing tech companies. The state then created a committee to study data privacy, which was populated in large part by industry representatives.
Facebook declined to answer questions on the record for this story.
The ones that were most interested were primarily the big tech companies. I received significant opposition to making any changes.
Rep. Giovanni Capriglione, Texas state House of Representatives
Capriglione introduced another privacy bill in 2021, but given “Texas’s conservative nature,” he said, and the previous pushback, it doesn’t include any opt-in or opt-out requirement or a private right of action. But he has still received pushback from industry over issues like how clear and understandable website privacy policies have to be.
“The ones that were most interested were primarily the big tech companies,” he said. “I received significant opposition to making any changes” to the status quo.
Washington
The privacy bill furthest along of all pending bills is in Washington, the home state of Microsoft and Amazon. The Washington Privacy Act was first introduced in 2019 and was the inspiration for Virginia’s law. Microsoft, Amazon, and more recently Google, have all testified in favor of the bill. It passed the state Senate 48–1 in March.
A House committee considering the bill has proposed an amendment that would create a private right of action, but it is unclear whether that will survive the rest of the legislative process.
Other States
Other states—Illinois, Kentucky, Alabama, Alaska, and Colorado—have Virgina-like bills under consideration. State representative Michelle Mussman, the sponsor of a privacy bill in Illinois, and state representative Lisa Willner, the sponsor of a bill in Kentucky, told The Markup that they had not consulted with industry or made privacy legislation their priority during 2021, but when working with legislative staff to author the bills they eventually put forward, they looked to other states for inspiration. The framework they settled on was significantly similar to Virginia’s on key points, according to The Markup’s analysis.
The sponsors of bills in Alabama, Alaska, and Colorado did not respond to interview requests, and public hearing testimony or lobbying records in those states were not yet available.
The Campaign Against Tougher Bills
In North Dakota, lawmakers in January introduced a consumer data privacy bill that a coalition of advertising organizations called “the most restrictive privacy law in the United States.” It would have included an opt-in framework, a private right of action, and broad definitions of the kind of data and practices subject to the law.
It failed 75–19 in the House shortly after a public hearing in which only AT&T, data broker RELX, and industry groups like The Internet Association, TechNet, and the State Privacy and Security Coalition showed up to testify—all in opposition. And while the big tech companies didn’t directly testify on the bill, lobbying records suggest they exerted influence in other ways.
The 2020–2021 lobbyist filing period in North Dakota, which coincided with the legislature’s study and hearing on the bill, marked the first time Amazon has registered a lobbyist in the state since 2018 and the first time Apple and Google have registered lobbyists since the state began publishing lobbying disclosures in 2016, according to state lobbying records.
A Mississippi bill containing a private right of action met a similar fate. The bill’s sponsor, Sen. Angela Turner-Ford, did not respond to an interview request.
While in Florida, a bill that was originally modeled after California’s laws has been the subject of intense industry lobbying both in public and behind the scenes. On April 6, a Florida Senate committee voted to remove the private right of action, leaving a bill substantially similar to Virginia’s. State senator Jennifer Bradley, the sponsor of Florida’s bill, did not respond to The Markup’s request for comment.
Several bills that include opt-in frameworks, private rights of action, and other provisions that experts say make for strong consumer protection legislation are beginning to make their way through statehouses in Massachusetts, New York, and New Jersey. It remains to be seen whether those bills’ current protections can survive the influence of an industry keen to set the precedent for expected debate over a federal privacy law.
If the model that passed in Virginia and is moving forward in other states continues to win out, it will “really hamstring federal lawmakers’ ability to do anything stronger, which is really concerning considering how weak [that model] is,” said Jennifer Lee, the technology and liberty project manager for the ACLU of Washington. “I think it really will entrench the status quo in allowing companies to operate under the guise of privacy protections that aren’t actually that protective.”